Imagine you are standing at the edge of a deep, treacherous chasm. On the other side, lies the fulfillment of your hopes and dreams, but to reach it, you must rely on someone else to build a sturdy bridge and guide you safely across. This reliance on another party is akin to the concept of counterparty risk. In the world of finance, counterparty risk refers to the chance that a party fails to fulfill its obligations, leading to potential economic loss.
It is a critical aspect of credit risk, encompassing both issuer and counterparty credit risks. Understanding and managing counterparty risk is of utmost importance to businesses and investors alike. In this article, we will delve into the causes and types of counterparty risk, explore strategies for managing and mitigating it, and discuss the significance of counterparty risk in various investment scenarios. Join us as we navigate the intricate landscape of counterparty risk and discover ways to safeguard against its potential pitfalls.
Key Takeaways
- Counterparty risk refers to the chance of a party failing to fulfill its obligations, leading to potential economic loss.
- Counterparty risk is particularly important in complex financial instruments like derivatives.
- Factors such as financial strength, industry reputation, and collateral can mitigate counterparty risk.
- Effective risk management strategies, such as diversification of counterparties and requiring collateral, can help mitigate counterparty risk.
What is Counterparty Risk?
Counterparty risk refers to the likelihood of a party failing to fulfill its obligations and is a subset of credit risk that encompasses various types of economic loss, including default and settlement risks. It is a crucial aspect of financial transactions as it evaluates the potential for losses arising from the actions or inactions of counterparties. Understanding counterparty risk is vital for individuals and businesses engaging in financial agreements, as it helps assess the probability of default and potential loss.
Counterparty risk is particularly important in complex financial instruments, such as derivatives, where the failure of one party to honor its contractual obligations can have significant consequences. By considering factors such as financial strength, industry reputation, and collateral, one can mitigate counterparty risk and make informed decisions about engaging with counterparties.
Causes and Types of Counterparty Risk
One factor that contributes to the potential for default in financial transactions is the financial strength of the involved parties. Counterparty risk can arise from various causes and can have significant impacts on financial transactions. One cause of counterparty risk is the financial weakness of a counterparty, which increases the likelihood of default. Another cause is the reputation of the counterparty within the industry, as a poor reputation can signal a higher risk of default.
| Cause of Counterparty Risk | Type of Counterparty Risk |
|---|---|
| Credit Risk | Default Risk |
| Credit Downgrade Risk | |
| Credit Spread Risk | |
| Settlement Risk | Herstatt Risk |
| Delivery Risk | |
| Timing Risk | |
| Market Risk | Price Risk |
| Interest Rate Risk | |
| Currency Risk | |
| Commodity Price Risk | |
| Operational Risk | Legal and Regulatory Risk |
| System and Technology Risk | |
| Settlement and Custody Risk | |
| Reputational Risk | |
| Counterparty Exposure Risk | Concentration Risk |
| Counterparty Size Risk | |
| Netting and Collateral Risk | |
| Country and Sovereign Risk |
Additionally, the absence or insufficiency of collateral can also contribute to counterparty risk. The impact of counterparty risk can be substantial, leading to financial losses and disruptions in the settlement process. It can also affect market confidence and liquidity. Therefore, it is crucial for market participants to assess and manage counterparty risk effectively to mitigate potential losses and maintain stability in financial markets.
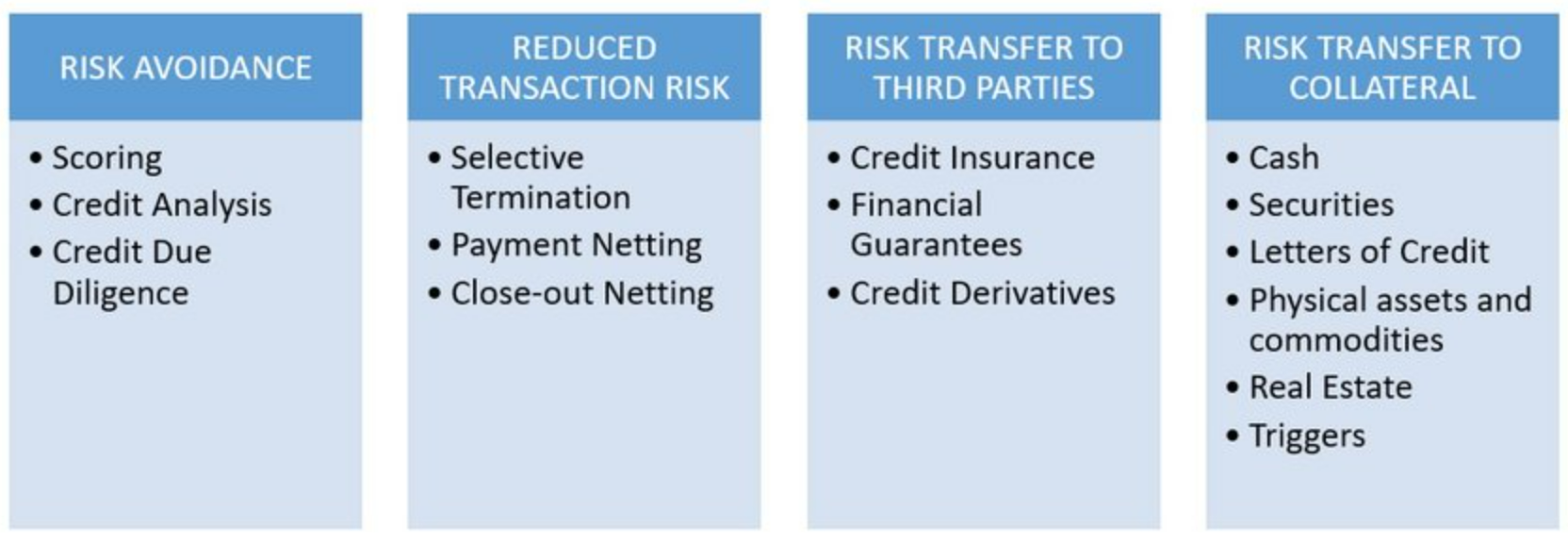
Managing and Mitigating
To effectively manage and mitigate the potential negative consequences of counterparty risk, market participants must implement robust risk management strategies and protocols. These strategies aim to assess and evaluate the level of risk associated with counterparties, and to develop appropriate measures to mitigate and control that risk. Some key risk management strategies for managing counterparty risk include:
- Diversification: Diversifying counterparties and spreading exposure across multiple entities can help reduce the concentration of risk. This approach ensures that a potential default by one counterparty does not have a significant impact on the overall portfolio.
- Collateralization: Requiring counterparties to post collateral can provide an additional layer of protection against potential defaults. Collateral assets can be liquidated in the event of default to cover the losses incurred.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Regular monitoring and reporting of counterparty creditworthiness and financial strength is crucial for identifying emerging risks. This allows market participants to take timely actions to mitigate potential losses.
By implementing these risk management strategies, market participants can better assess and control counterparty risk, reducing the likelihood of financial losses and ensuring the overall stability and resilience of their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does counterparty risk impact financial institutions?
Counterparty risk has a significant impact on financial institutions, necessitating robust risk management strategies. The exposure to potential default by counterparties can lead to adverse consequences such as financial losses and reputational damage. Financial institutions must carefully evaluate and monitor counterparty creditworthiness to mitigate these risks.
Additionally, counterparty risk can have implications for credit ratings, as a higher level of risk can result in downgrades, making it more challenging and costly for institutions to access capital. Therefore, effective management of counterparty risk is crucial for maintaining financial stability and credibility.
What are the potential consequences of a counterparty default?
The potential consequences of a counterparty default can be significant for financial institutions. In the recovery process, the institution may face challenges in obtaining the owed funds or collateral, which can result in financial losses.
Legal implications may arise, such as litigation or arbitration, to enforce contractual obligations. These consequences can harm the institution’s financial stability and reputation, impacting its ability to attract investors and conduct future business transactions. Therefore, managing counterparty risk is crucial to mitigate these potential negative outcomes.
Are there any regulatory requirements or guidelines for managing counterparty risk?
Regulatory oversight plays a crucial role in managing counterparty risk, providing guidelines and requirements that promote effective risk management strategies. Financial regulatory authorities, such as the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, have implemented frameworks and standards, such as the Basel Accords, to ensure banks and financial institutions assess, monitor, and mitigate counterparty risk.
These guidelines focus on factors such as capital adequacy, risk measurement, and risk management practices. By adhering to these regulatory requirements, institutions can enhance their ability to identify and manage counterparty risk effectively.
How can companies assess the financial strength of a counterparty?
Assessing counterparty risk involves evaluating the financial stability of a counterparty. Companies can use various methods to assess the financial strength of a counterparty. These methods include analyzing financial statements, credit ratings, and conducting due diligence. Financial statements provide insight into a counterparty’s financial health, while credit ratings assess their creditworthiness.
Due diligence involves conducting a comprehensive review of the counterparty’s financial records, business operations, and industry reputation. By employing these methods, companies can make informed decisions regarding the level of counterparty risk they are willing to accept.
Can counterparty risk be completely eliminated or only mitigated?
Counterparty risk cannot be completely eliminated, but it can be mitigated through risk management strategies. These strategies aim to reduce the probability of default and potential loss associated with counterparty risk.
Examples of risk mitigation strategies include conducting thorough due diligence on counterparties, diversifying counterparties to reduce concentration risk, requiring collateral or guarantees, and implementing robust risk monitoring and reporting systems. While these measures can significantly reduce counterparty risk, it is important to note that no strategy can completely eliminate it. Therefore, businesses must continuously assess and manage counterparty risk to protect their financial interests.