
Are you looking for a bearish options strategy that can potentially maximize your profits? Look no further than the short call option strategy. This strategy is designed for bearish and neutral markets, allowing you to sell call options with the expectation that the underlying stock price will decrease or remain stagnant. The short call strategy offers the potential for significant profit, but it also carries the risk of unlimited loss.
In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of the short call strategy, including its profit potential, loss potential, and real trade examples. By using visuals graphs, we will illustrate the performance of this strategy in different historical scenarios, showcasing both profitable and loss-making trades. Whether you’re an experienced trader or just starting out, the short call option strategy is a valuable tool to add to your trading arsenal.
Key Takeaways
- Short call option strategy is best suited for bearish and neutral markets.
- Maximum profit in a short call strategy is the total credit received.
- Short calls can profit in any market, including minorly bullish markets.
- It is important to monitor the position and secure profits when appropriate in short call strategy.
What is Short Call Option Strategy?
The short call option strategy is a bearish options strategy that is best suited for bearish and neutral markets. It offers a maximum profit potential equal to the total credit received and an unlimited maximum loss potential. This strategy involves selling call options on a stock that the trader does not own, with the expectation that the stock price will decrease or remain stagnant.
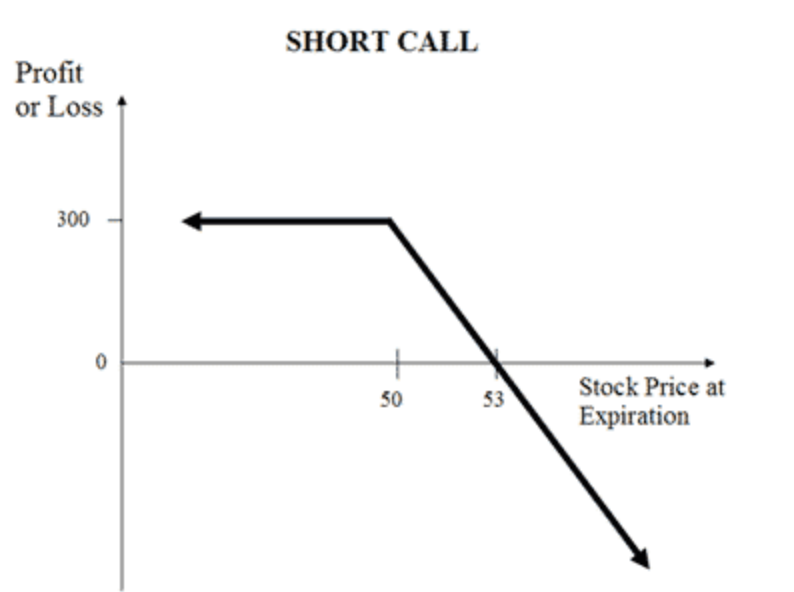
Advantages of the short call strategy include the ability to profit in any market, including minorly bullish markets, and the potential for slow and steady profits through time as options extrinsic value decays. However, there are also disadvantages to consider, such as the unlimited maximum loss potential and the need to monitor the position and secure profits when appropriate.
Suitable market conditions for the short call strategy are bearish and neutral markets, where the trader expects the stock price to decrease or remain stagnant. It is important to assess the market conditions and the potential risks before implementing this strategy.
Short Call Option: Profit Potential
Profit potential in the short call strategy is akin to a vast ocean, with the trader’s earnings limited only by the total credit received. However, it’s crucial to consider the breakeven price and implement effective risk management strategies. Here are five key points to understand about the profit potential in a short call strategy:
- Maximum profit is achieved when the stock price remains below the strike price, resulting in the call option expiring worthless and the trader realizing the maximum profit potential.
- The breakeven price is the strike price plus the credit received. If the stock price at expiration is equal to the breakeven price, the trader breaks even on the trade.
- Short calls can still profit in minorly bullish markets, as long as the stock price remains below the strike price and the call expires worthless.
- It is important to monitor the position and secure profits when appropriate, as the maximum loss potential in a short call strategy is unlimited.
- Risk management is crucial in short call positions, as unexpected stock price movements can result in significant losses. Traders should consider implementing stop-loss orders or adjustments to limit potential losses.
Loss Potential
Loss potential in the short call strategy is a critical aspect to consider, as it is unlimited and can result in significant losses if the stock price moves above the strike price. Managing risk in the short call strategy is essential to protect against potential losses. Several factors can affect the maximum loss potential in the short call strategy. These factors include the distance between the strike price and the current stock price, the time remaining until expiration, and the volatility of the underlying stock.
Traders need to monitor the position closely and adjust their strategy if necessary to limit potential losses. It is crucial to have a plan in place for closing the position or implementing risk management techniques, such as using stop-loss orders or rolling the position to a higher strike price. By actively managing risk, traders can mitigate the unlimited loss potential in the short call strategy.
| Factors affecting maximum loss potential in short call strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Distance between strike price and current stock price | A larger distance between the strike price and the current stock price increases the maximum loss potential. |
| Time remaining until expiration | As time passes, the maximum loss potential decreases, as the option’s extrinsic value decays. |
| Volatility of the underlying stock | Higher volatility increases the maximum loss potential, as it increases the likelihood of the stock price moving above the strike price. |
| Risk management techniques | Implementing risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders or rolling the position to a higher strike price, can help limit potential losses. |
Real Trade Examples of Short Call Option Strategy
Real trade examples can provide valuable insights into the historical performance of the short call strategy. These examples showcase different scenarios and demonstrate the potential outcomes of implementing this strategy. It is crucial for traders to understand the importance of monitoring and managing their short call positions. By closely monitoring the stock price and market conditions, traders can make informed decisions to secure profits or minimize losses.
| Trade | Stock | Option Type | Strike Price | Expiration Date | Premium Received | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ABC | Short Call | $110 | 2023-09-01 | $2.50 | Stock price stays below $110 by expiration, and the option expires worthless. The trader keeps the $2.50 premium as profit. |
| 2 | XYZ | Short Call | $95 | 2023-09-01 | $1.75 | Stock price stays above $95 by expiration, and the option is exercised. The trader sells the stock at $95 and keeps the $1.75 premium as profit. If the stock price goes significantly above $95, the trader might incur losses. |
| 3 | DEF | Short Call | $105 | 2023-09-01 | $3.20 | Stock price stays below $105 by expiration, and the option expires worthless. The trader keeps the $3.20 premium as profit. |
The examples highlight the risks involved in selling call options and emphasize the need for active management. By analyzing the historical performance of the short call strategy through real trade examples, traders can gain a better understanding of its potential profitability and the importance of effective position management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any alternative options strategies that can be used in bearish and neutral markets?
Alternative options strategies that can be used in bearish and neutral markets include the long put option strategy and the bear put spread strategy. The long put option strategy allows investors to profit from a decline in the underlying asset’s price.
On the other hand, the bear put spread strategy involves buying a put option with a higher strike price and selling a put option with a lower strike price. These strategies can provide opportunities for investors to profit in bearish and neutral market conditions.
How can I calculate the breakeven point for a short call position?
To calculate the breakeven point for a short call position, one must consider the strike price and the credit received. The breakeven point is reached when the stock price equals the strike price plus the credit received.
Understanding profit potential in a short call position is crucial, as it allows traders to assess the potential gains and losses. The maximum profit for a short call is the total credit received, while the maximum loss is unlimited.
What factors should I consider when deciding whether to close a short call position for a profit?
When deciding whether to close a short call position for a profit, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, calculating profit potential is crucial. Traders should assess the current value of the short call option and compare it to the initial credit received. If the option’s value has significantly decreased, it may be a good opportunity to close the position and secure profits.
Additionally, understanding time decay is important. As time passes, options lose their extrinsic value, which can work in favor of short call positions. Traders should monitor the option’s time decay and consider closing the position when a substantial portion of the option’s extrinsic value has decayed.
Can the short call strategy be applied to options on any type of asset, or is it limited to stocks?
The short call strategy can be applied to options on various types of assets, not just limited to stocks. While the guide primarily focuses on stocks, the underlying principle of the strategy remains the same for other assets such as commodities or currencies.
The short call strategy involves selling call options with the expectation that the price of the underlying asset will decrease or remain stagnant. It is important to note that the short call strategy is just one of many options strategies available, each with its own advantages and considerations.
What are some common risks and challenges associated with selling call options?
Selling call options, oh what a breeze! But hold on, there are risks and challenges you must seize. The potential drawbacks of the short call strategy lie in its unlimited loss potential. Yes, you heard it right, unlimited losses can take flight.
The short call position can turn sour if the stock price unexpectedly rises above the strike. So, be analytical, data-driven, and well-informed. Monitor your position diligently, or else your profits may be deformed.


